Glaucoma – A Serious Eye Condition
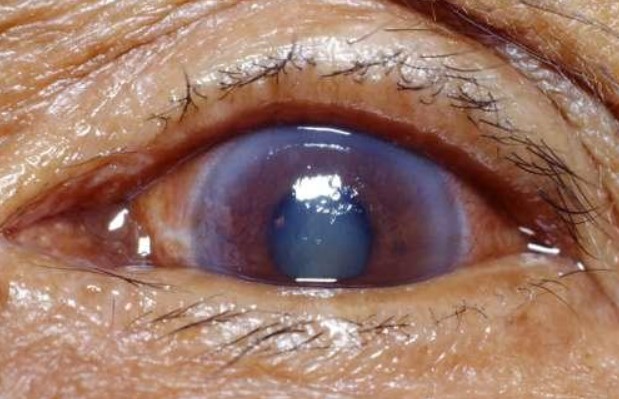
Intraocular pressure increases within the eyeball as a result of glaucoma, a serious condition of the eyes. The condition is similar to high blood pressure in the body. Therefore, hypertension of the eye is the name given to this condition. Intraocular pressure is necessary to prevent eye damage, but too much can result in vision loss. Blindness among adults is primarily caused by glaucoma. Blind people are more likely to suffer from glaucoma than those who aren’t. The disease is more likely to be developed by farsighted people than by nearsighted people.
Symptoms
Glaucoma appears as colored rings or halos around distant objects at night, as the first symptom of the disease. Usually, the iris is protruding forward, and the patient suffers constant pain near the temples and cheeks as well as the brow. Most people experience headaches at some point in their lives. Glaucoma gradually impairs vision as it develops, and if it is not treated in time, it may eventually result in blindness.
Causes
As a result of severe eye strain or prolonged exposure to poor lighting conditions, glaucoma is considered to be one of the most common causes of blindness. Yet, in reality, glaucoma is primarily caused by vitamin deficiencies, poor lifestyle choices, and prolonged drug use to treat other diseases that is highly toxic to the system. Only eye strain contributes to this condition. Chronic stress can also lead to glaucoma, which is usually a result of adrenal exhaustion.
As a result of the adrenal glands’ incapacity to produce aldosterone, the body loses salt excessively and fluid accumulates in the tissues. Eyeballs harden when excess fluid accumulates in the region, causing them to lose their softness and resilience. As well as those described above, glaucoma is associated with giddiness, sinusitis, allergies, diabetes, hypoglycemia, arteriosclerosis, and a malfunctioning of the autonomic nervous system.