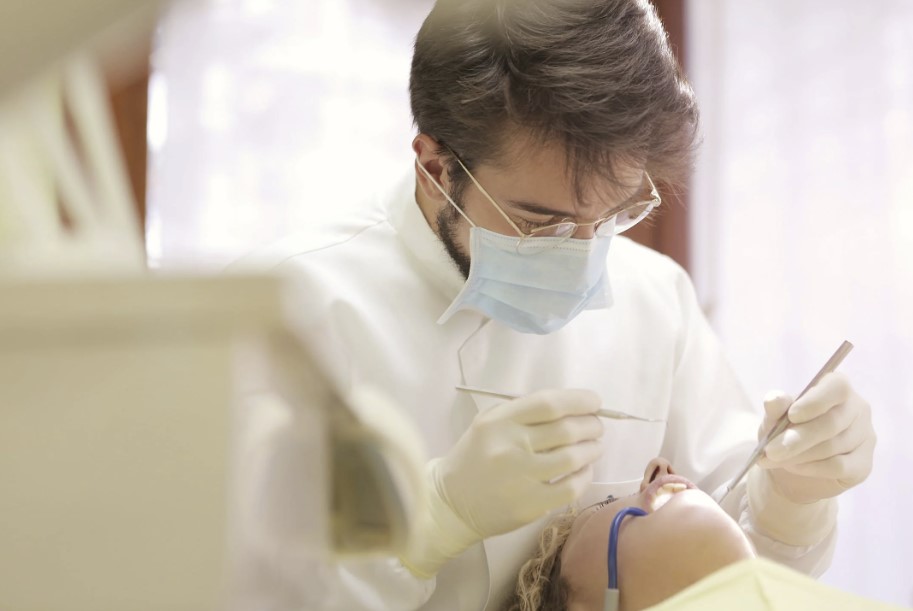
Gum disease, also known as gingivitis, is a condition in which the gums become swollen and red, bleeding easily after brushing or eating. The condition is caused by deep pockets forming between the gums and teeth, allowing bacteria to accumulate. This causes gum disease, which leads to tissue decay. When the tooth has no more tissue to hold onto, it must be removed and eventually lost permanently.
Gum Disease and Periodontitis
There is a difference between gingivitis and periodontitis, which are both called gum diseases. The main characteristic of gingivitis is gum inflammation. After brushing or flossing, the pockets start to form, causing sensitivity and bleeding.
An advanced stage of gum disease, periodontitis is caused by inflammation. If you notice any symptoms of gum inflammation, you should be vigilant since gingivitis does not always lead to periodontitis. Generally, gum disease is used to describe periodontitis.

Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease can be caused by a variety of factors. The first thing you should do is brush and floss your teeth infrequently or never. This condition is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows tartar to build up. Neglecting this for a long period of time may result in irreversible damage. Gum disease is most likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Imbalance of hormones – Pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can all cause hormonal imbalance. It is during this time that the gums become more sensitive, making them more susceptible to bacterial infection.
The importance of nutrition in maintaining gum health is often overlooked. It can be more difficult for the body to fight off infection if it consumes a diet that lacks key nutrients. It is critical to remember that periodontal disease is caused by an infection and can be made worse by a poor diet. Periodontal disease may also be associated with obesity, according to research.
Smoking
It is imperative to avoid smoking because it compromises the health of your mouth by making it harder for your gums to heal and self-repair. Furthermore, nicotine increases tartar buildup, which only speeds up bacteria growth and plaque spread.
Immune System Issues
Healing is more difficult when you have a health problem says this experienced dentist in Henderson. There is no exception when it comes to gum disease, which encompasses practically all health issues. AIDS, HIV, and cancer are known to compromise the immune system. Gum disease may also be associated with diabetes.
Medications
Medication side effects that cause dry mouth syndrome may also increase the risk of the said condition. Since saliva inhibits the growth of bacteria, it is wonderful for maintaining oral health. Gums are more likely to become infected with bacteria when they are dry.
Main Symptoms of Gum Disease
There are many factors that contribute to gum disease or gingivitis. Gingivitis is most commonly caused by poor oral hygiene, stress, and smoking. Gingivitis causes bleeding, redness, swelling, and offensive breath, as well as tooth sensitivity to temperature changes or sweets.
Gingivitis is a common cause of tooth loss among adults, and if left untreated can lead to periodontal disease. The symptoms of gum disease are numerous, and most of them can be observed by looking in the mirror. If you want to know if you have one, look for these signs:
-
Pockets between teeth and gums that are reddish in color
-
During brushing or flossing, gums often bleed easily.
-
Receding gums
-
Teeth start shifting, causing their position to change. When dentures no longer fit properly or have gaps, this becomes apparent.
-
Even after brushing, you have a funny taste in your mouth or a constant smell on your breath
-
Symptoms include swollen and red gums.
-
When you are exposed to hot or cold temperatures, your teeth become more sensitive.
Of course, your dentist can give you a better idea of how severe gum disease is at this point. This is why a routine checkup will allow you to quickly discover the problem so you can apply methods to reverse the damage. Further diagnosis may be performed to determine the extent of the damage.
Gum Disease: How Severe Is It?
Your dentist measures the pockets between the teeth and the gums to determine the stage of your gum disease. Measurements typically range from 1 to 3 mm. If the pockets exceed 5mm, the dental intervention will be required to prevent further damage. Additionally, your dentist will request x-rays to determine the extent of the damage.
Read More – How to a Get Healthy Teeth Whitening Smile?