What is Pichia pastoris and why is it Useful?
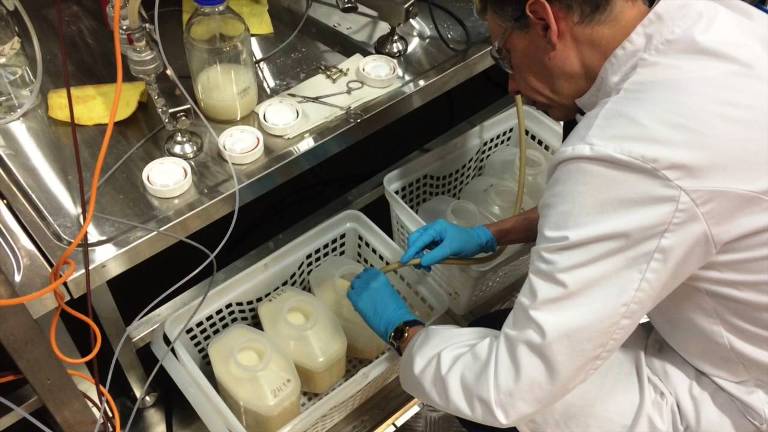
Pichia pastoris (or Komagataella phaffii) is a species of yeast that is widely used in the production of recombinant proteins and other biomolecules. A yeast starter culture is a small amount of liquid containing yeast that is used to start a batch of beer or wine. The culture can be kept for months and years by adding sugar to the starter and keeping it in the fridge. Heterologous proteins and metabolites are produced by yeasts.
It is a filamentous fungus that grows well on glucose, ethanol, glycerol, and other sugars. The most famous use for Pichia pastoris is the production of recombinant proteins in the laboratory. It has been used in the production of insulin, human growth hormone, and other medicines.
Unlike Escherichia coli or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris is a suitable eukaryotic platform for protein expression and biofuel production.
There are many health benefits associated with Pichia Pastoris. Digestion, the immune system, heart health, and brain function can all be improved with it. Cultivating Pichia Pastoris is not difficult at all. Water, flour, salt, sugar, and yeast starter culture are the only ingredients you need.
Expression host: Pichia pastoris
Biopharmaceuticals and industrial enzymes are mostly produced using Pichia pastoris as an expression host. It is a methylotrophic, facultatively anaerobic, chemoheterotroph yeast. This yeast has a typical yeast structure, with a wall thickness of 15 microns and a width of 15 microns. P. pastoris is a mesophilic microorganism that lives at temperatures between 25 and 35 degrees Celsius. It also grows at a very wide range of pH values between 3.0 and 7.0, which is another advantage of P.pastoris.
P. pastoris does not secrete or produce every protein of interest at such a high level. Many complex proteins, particularly those that are oligomers, membrane-attached, or prone to proteolytic degradation, yield low yields.
Advantages
-
Among the many benefits of P.pastoris over other microorganisms, there are the following advantages.
-
Unlike Saccharomyces cerevisiae, P. pastoris has a strong preference for respiratory metabolism. A proton-translocation complex resides in the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
-
A very high cell density combined with the ability to grow on a minimal medium. Pichia processes use simple chemically defined mediums with inexpensive formulations as the production medium. It is capable of producing large amounts of extracellular proteins, facilitating subsequent purification.
-
A eukaryotic cell has several advantages; it is genetically easy to manipulate and has the eukaryotic protein synthesis pathway that enables post-translational modifications.
-
The most significant feature of P. pastoris is that alcohol oxidizes one promoter (AOX1), the strongest negatively regulated promoter known. As methanol induces protein production through AOX1 promoter, it acts both as a carbon source and inducer. Over the years, hundreds of proteins have been produced by P.pastoris. As the most common method for heterologous protein expression in P. pastoris, the target gene is inserted into the genome under the control of the alcohol oxidase 1 promoter (pAOXI). It offers tight regulation as well as a very strong, methanol-inducible reaction. Furthermore, it is nonpathogenic and does not produce endotoxins.
-
pastoris has very low substrate requirements for maintenance at slow growth rates. In the production of proteins and metabolites, ATP is required for the synthesis of sugar-based proteins and metabolites.
-
Moreover, P. pastoris is a suitable candidate for developing zero-growth cell factory concepts due to its tolerance to caloric restriction. There has been very little comparative research done to quantify maintenance-energy requirements in different microorganisms, despite their impact on productivity and product yields in large-scale, aerobic fed-batch processes.
-
Through retentiontostat cultivation, a powerful tool can be used to identify and comprehend the molecular basis for these diverse requirements in industrially relevant microorganisms. On the other hand, one significant disadvantage of Pichia fermentation is the slower growth rate of the yeast compared with bacteria; hence the cultivation durations are longer. Using methanol as a carbon source is also a disadvantage since it is a hazardous petrochemical substance.
Pichia Pastoris Carbon Source Utilization Pathways
Fermentations of P. pastoris follow a standard protocol with two phases, such as growth and production. Glycerol is the sole carbon source before protein synthesis (methanol induction) in order to reach maximum cell densities. Due to the higher specific growth rate of glycerol over methanol, it is fed into the reactor once the glycerol has been depleted.
The basis for the P. pastoris expression procedure arises from the finding that some of the enzymes that are required for the methanol utilization pathway are only present in substantial amounts only if the cells are grown on methanol. For the improvement of production efficiency in achieving higher recombinant protein concentrations, during the production phase, the use of several other carbon sources in addition to methanol has been investigated.
Alcohol Oxidase Promoter and Methanol Utilization Phenotypes
The production of recombinant proteins requires a strong and tightly regulated AOX1 promoter, as already mentioned. AOX1 has the advantage of tightly controlling protein transcription. Through the depression/ re-depression mechanism, one can achieve high levels of production. By repressing transcription, the carbon source (glycerol) results in a higher concentration of cells before production begins.
A shift in metabolic reactions toward growth reactions is directly linked to an increase in cell concentration when cells are not producing products. P.pastoris, however, uses methanol, a hazardous chemical, which is the major problem. Methanol monitoring also poses problems. The sole carbon and energy source of P. pastoris is methanol.
Oxygen Transfer
Through the fermentation process, Pichia pastoris uses oxygen up to a certain level as a facultative anaerobic microorganism. Oxygen affects metabolic pathways. Depending on the organism’s metabolism and environment, oxygen requirements differ between microorganisms. As yeast, P. pastoris is able to use oxygen to produce energy during respiration (oxidative phosphorylation) and to synthesize fatty acids and sterols. P.pastoris is an expression host in that it prefers respiratory pathways instead of fermentation. This is because it produces a relatively low amount of ethanol and acetic acid.
Due to the fact that oxygen is also used to oxidize methanol to formaldehyde in a side reaction, there is a requirement for higher oxygen transfer rates for the methanol utilization pathway, which results in the formation of the product. Oxygen transfer resistances are minimized by high agitation, and oxygen-enriched air is usually used to provide the required amount of oxygen.
Purification of Human Growth Hormone
As the final aim of rhGH production is to implement the clinical use of this product as a therapeutic agent, it is very imperative to achieve high purity. Depending on the host microorganism selected for rhGH production the protein can be produced extracellularly or intracellularly (in E. coli by inclusion bodies). RhGH is primarily found in fermentation broth along with some fermentation byproducts (like proteases and other host-cell proteins), salts, organic/amino acids, or even in an intracellular medium containing even more complicated components.
Some of these medium constituents can be removed by desalting or ultrafiltration using the proper membranes, but other purification techniques based on affinity separation are necessary as well. RhGH was purified using a variety of methods including ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and metal chelate affinity chromatography.







