- Magnificent Hummingbird was formerly known as Rivoli’s Hummingbird after François Victor Masséna, the second Duke of Rivoli, who was renowned as an amateur ornithologist during the 19th century.
- While the tail of females is less white and greener than that of female Blue-throated Hummingbirds, the head is similar. Its underparts are dark and scaly, and its crown and gorget are covered in bright iridescence. It is intermediate between females and adult males.
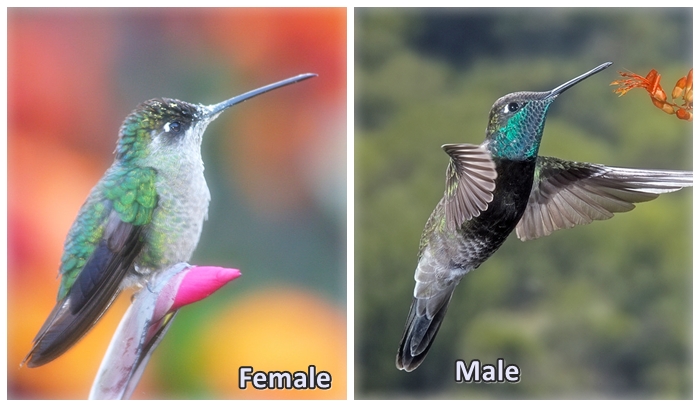
Rivoli’s hummingbird: male and female. Photo Credit: Wikipedia - In dry forests, northern birds forage on many small flower patches over the course of a day, whereas southern birds tend to be territorial.
- While migratory in northern populations, some individuals frequent feeding stations throughout the year in the southwest. Populations in Costa Rica and Panama are larger and paler than those of northern birds and are sometimes considered a separate species, the Admirable Hummingbird (Eugenes spectabilis).
- The habitats of the Magnificent Hummingbird are mountain conifer, oak, and mixed forest; 5,000–9,750 ft, often lower during migration and in winter.
- The Magnificent Hummingbird is about 13–14 cm in length with a weight of 5.5–9.5 g.
- Depending on the season, elevation, and latitude, Rivoli’s hummingbirds feed on nectar from a variety of flowering plants. The species is not aggressive when it comes to hummingbirds at flowers or feeders, regardless of their size. By sucking nectar from its very long bill, the bird “traplines” between patches of flowers spaced widely apart.
- There is no record of a higher heart rate in any vertebrate than that of the Magnificent Hummingbird, which ranges from 420 to 1,200 beats per minute.
- Hummingbirds of Rivoli’s hummingbird (Eugenes fulgens) belong to the tribe Lampornithini and subfamily Trochilinae, also known as “mountain gems”. Besides El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and the United States, it is also found in Belize and Mexico. Subsp. fulgens occurs in the southwestern United States, Mexico, Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. And subsp. spectabilis occurs in Costa Rica as well as in western Panama.
- Among Rivoli’s hummingbird songs are loud or high-pitched, sharp tchiks or tcheeps. Another possibility is “a short chatter that rises and falls”. As they perch and fly, males produce single- or multiple chip notes. A very rapid series of chip notes is given when the species acts aggressively or if it is alarmed.
Related Reading: Black Metaltail







