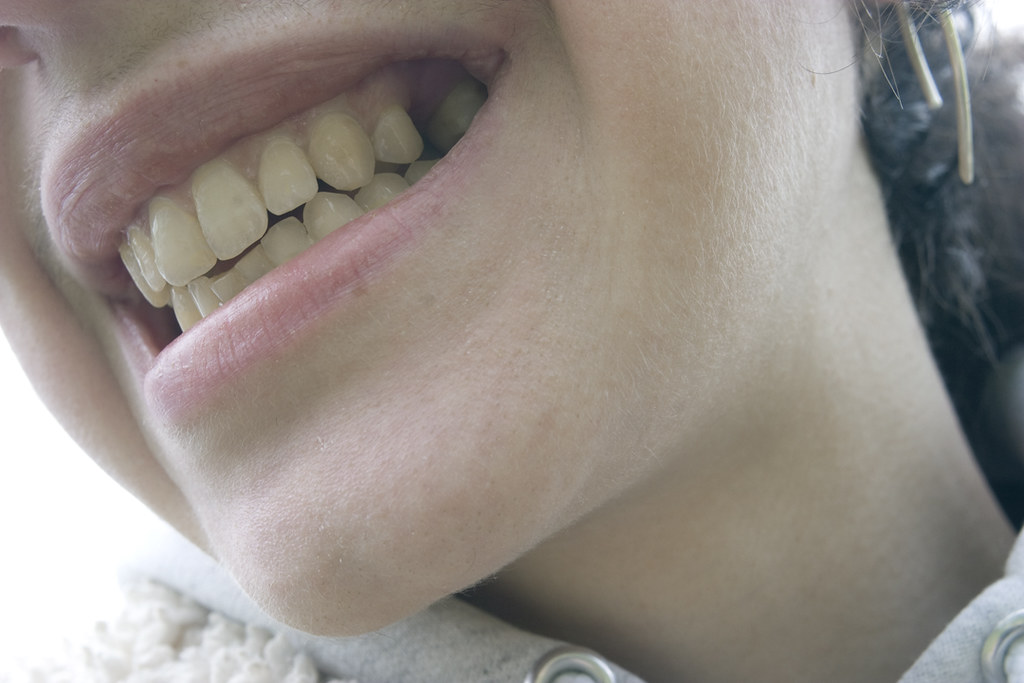
Breastfeeding and cavities is the most common question, nursing mothers ask. The nutrients in breast milk prevent tooth decay, so nighttime nursing does not cause it. There is no scientific basis for the assertion that nighttime nursing causes tooth decay, which is simply anti-breastfeeding propaganda.
Is breastfeeding really a cause of cavities? Breastfeeding is contradicted by the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD). According to their official policy, breastfeeding ensures the best development health, and psychosocial outcomes for children at all times of the day and night. Before the first teeth erupted, they recommended avoiding on-cue nighttime breastfeeding, but that no longer stands.
Tooth decay in toddlers’ front teeth, as breastfeeding a child after the first tooth erupts is not recommended by the AAPD policy since it can lead to cavities. All children should not breastfeed before and after the first tooth erupts. This idea does not appeal. Studies provided on their own website also do not support this concept.
According to AAPD, breast milk prevents acid and bacterial growth in the mouth, which means you should breastfeed your child to prevent cavities. The report notes that breast milk by itself does not contribute to cavities, but when breast milk is alternated with sweet foods, cavities are promoted.