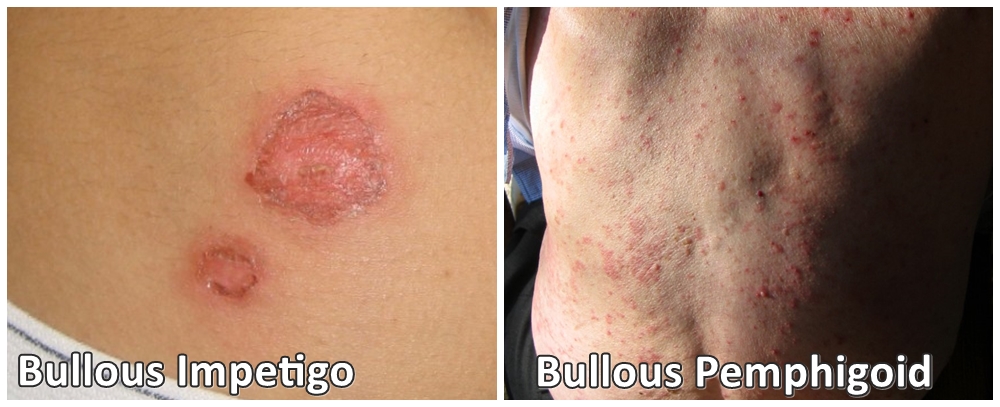
Bullous Impetigo vs Bullous Pemphigoid – Both are two distinct skin conditions that affect different layers of the skin, causing blistering and other symptoms. Bullous impetigo is a bacterial skin infection that typically affects young children. It is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, which produce toxins that cause the skin to blister and peel. The blisters usually appear in clusters and can be very itchy. They tend to be small and can rupture easily, causing yellow crusts to form. Bullous impetigo is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person through direct contact with the blisters.
Bullous pemphigoid, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is most commonly seen in elderly individuals and is caused by the immune system attacking the skin, resulting in blistering and peeling. The blisters tend to be larger and more widespread than those of bullous impetigo, and can appear anywhere on the body. Bullous pemphigoid blisters tend to be more persistent and may not rupture as easily as those of bullous impetigo. Other symptoms of bullous pemphigoid can include redness, itching, and inflammation of the affected areas.