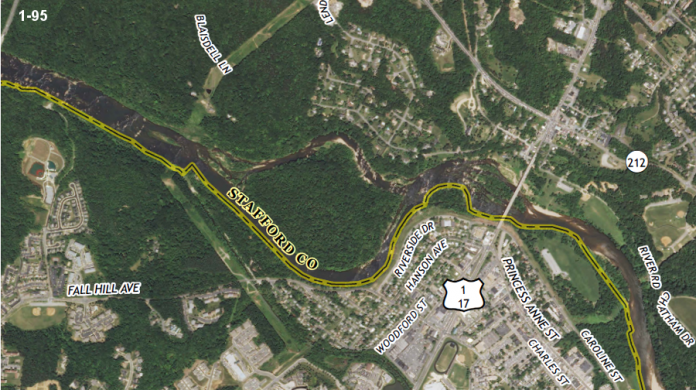
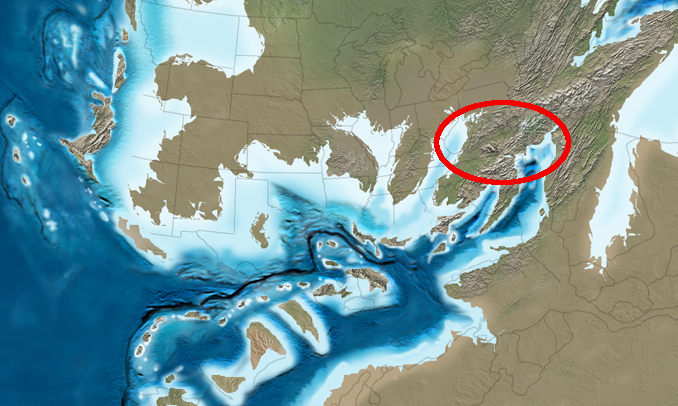
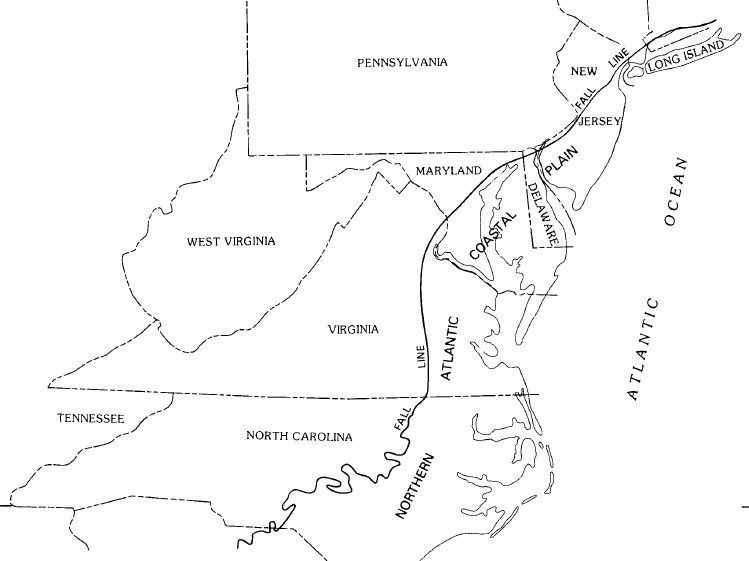
The Atlantic Seaboard Fall Line or ”Fall Zone”, is a 1,400 kilometers escarpment where the “Piedmont” and “Atlantic coastal” plain meet in the eastern United States. Much of the Atlantic Seaboard fall line passes across the areas where no evidence of faulting is available now. The fall line marks the geologic boundary of hard metamorphosed terrain “the product of the Taconic orogeny” and the sandy.
That is relatively flat outwash plain of the upper continental shelf, created of unconsolidated Cretaceous and Cenozoic sediments. The main examples of the Fall Zone comprise the “Potomac River’s Great Falls” and the rapids in Richmond, Virginia, where the James River falls across a series of rapids down to its own tidal estuary.
Before navigation improvements such as locks, the fall line was normally the head of navigation on rivers due to they’re fast-moving water or waterfalls, and the essential portage around them. The Great Falls of the Potomac River is one example. Due to the commercial traffic, requisite labor and accessibility of water power to operate mills; several cities were founded at the intersection of rivers and the fall line.
United States Route 1 connects several of the fall line cities. In 1808, Treasury Secretary “Albert Gallatin” noticed the importance of the fall line as a hindrance to improved national communication and commerce among the Atlantic seaboard and the western river systems. The most well-known, though not maybe the most challenging obstruction in the navigation of the Atlantic rivers, comprises in they’re lower falls, which are ascribed to a presumed incessant granite ridge, rising about 130 feet above tidewater.
Although, the ridge from New York to James River inclusively arrests the ascent of the tide; the falls of every river within that space being specifically at the head of the tide; following thence southwardly a direction almost parallel to the mountains, it recedes from the sea, leaving in each southern river a coverage of good navigation between the tide and the falls. Other falls of less magnitude are found at the gaps of the Blue Ridge, from side to side which the rivers have forced they’re passage.
Read About – Ketil Mountain – Most Challenging Big Walls on Earth
Source: Virginiaplaces and Wikipedia

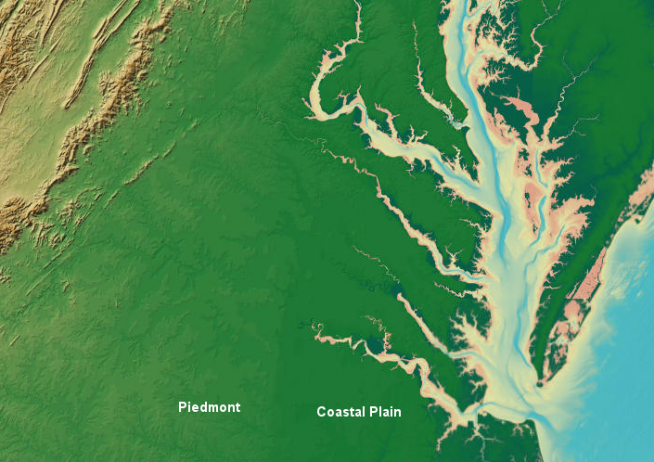
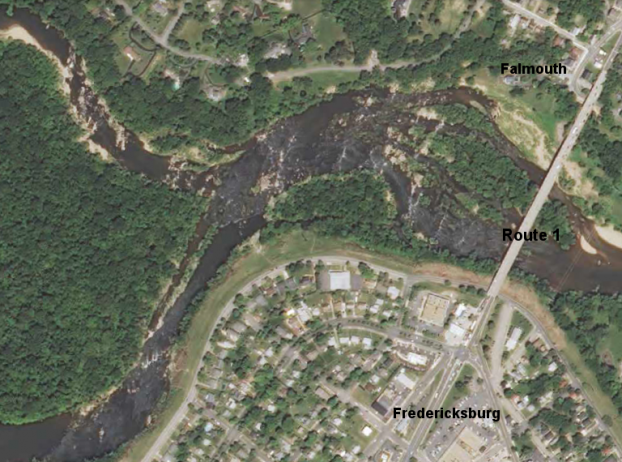
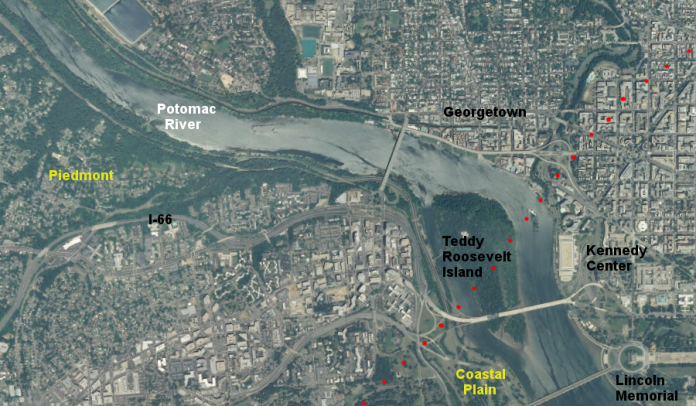

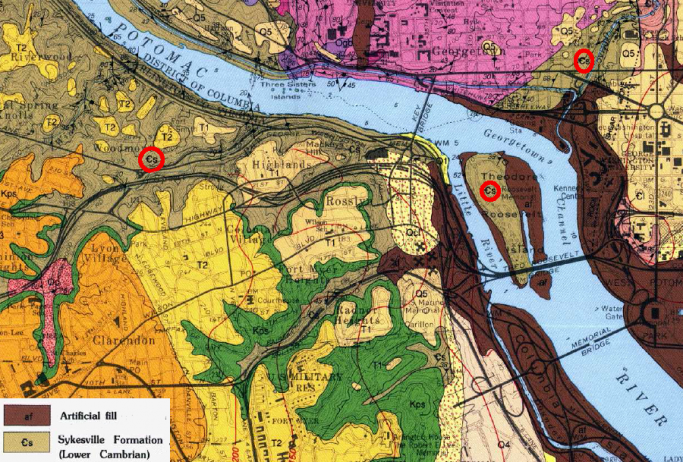
Great Falls, on the Potomac River, reveals the hard metamorphic rock of the Piedmont – and how rivers in flood stage carve channels